ONLINE BASIC COURSE
Cleanliness Analysis According to VDA 19.1 & ISO-16232
Part 2
Particle Extraction from Component Surface
The most common method for extraction of particles is rinsing the component surface with a fluid stream. The figure shows some typical rinsing scenarios for different component shapes.
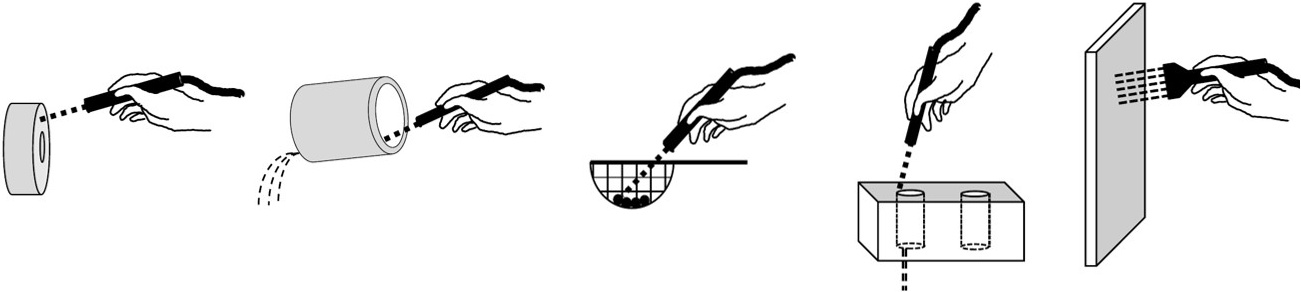
Extraction by rinsing for different component shapes (source VDA-19.1)
In addition, particle extraction using the following methods according to VDA-19.1 is possible:
- Extraction using an ultrasonic bath: This method is widely used and easily applicable in a laboratory. However, there may be problems with castings because the energy of the ultrasound damages the matrix of the cast material and creates additional particles. These distort the results of the cleanliness test.
- Internal purging by flow or by moving the liquid inside ("shaking"): These methods are used to remove particles from the interior surface of components.
- Particle extraction by blow off or throughflow of components with clean compressed air: This method is intended for components that are not exposed to any liquids during their functional use. However, the extraction by means of air flow is not yet used by default and its practicability has yet to be proven.
Surfactant water-based cleaning fluids are preferred for extraction as the liquid can be disposed of economically after use. However, the extraction effect of water-based cleaning fluids is often insufficient, especially if the component surface is contaminated with oily or fatty films. In this case, solvents based on cold cleaners are utilized. Cold cleaner fluids are typically regenerated after extraction, using a fine filtration system for reuse.
Navigator
Online Basic Course
- (1) Standardized Analysis of Component Cleanliness
- (2) Particle Extraction from Component Surface
- (3) Filtration of the Residual Particles
- (4) Equipment for Extraction and Filtration
- (5) Gravimetric Analysis of Particle Mass
- (6) Scanner and Microscope for Standardized Analysis
- (7) Optical Analysis of Residual Contaminant Particles
- (8) Particle Analysis from 50 Microns
- (9) Presentation of Particle Cleanliness
- (10) Residual Contaminant Analysis Using SEM-EDX
- (1) Standardized Analysis of Component Cleanliness
- (2) Particle Extraction from Component Surface
- (3) Filtration of the Residual Particles
- (4) Equipment for Extraction and Filtration
- (5) Gravimetric Analysis of Particle Mass
- (6) Scanner and Microscope for Standardized Analysis
- (7) Optical Analysis of Residual Contaminant Particles
- (8) Particle Analysis from 50 Microns
- (9) Presentation of Particle Cleanliness
- (10) Residual Contaminant Analysis Using SEM-EDX

